- Publication: JP Morgan
- Publication Date: January 1, 2023
- Organizations mentioned: J.P. Morgan Asset Management, Google, OpenAI
- Publication Authors: Michael Albrecht, Stephanie Aliaga
- Technical background required: Medium
- Estimated read time (original text): 57 minutes
- Sentiment score: 45%, somewhat negative (100% being most positive)
TLDR
Goal: The report, “The Transformative Power of Generative AI,” delves into how artificial intelligence (AI), especially generative AI, is poised to revolutionize work, innovation, and creativity. It emphasizes generative AI’s potential to become a “general-purpose technology,” akin to the steam engine and computer, with far-reaching implications for the global economy. This analysis is driven by the emerging role of AI in boosting labor productivity and reshaping job markets, set against a backdrop of recent stagnation in productivity growth.
Methodology:
- The report synthesizes a range of data and forecasts to assess the economic and labor impacts of AI.
- It utilizes generative AI’s capabilities, even in drafting parts of the paper, to demonstrate its practical applications and versatility.
- The analysis includes projections of labor productivity growth and evaluations of AI’s influence on job displacement and creation.
Key Findings:
- Economic Growth and Productivity: Generative AI is projected to significantly accelerate labor productivity, potentially increasing it by 1.5%-3.0% annually worldwide over the next decade. This boost is expected to parallel similar increases in real GDP.
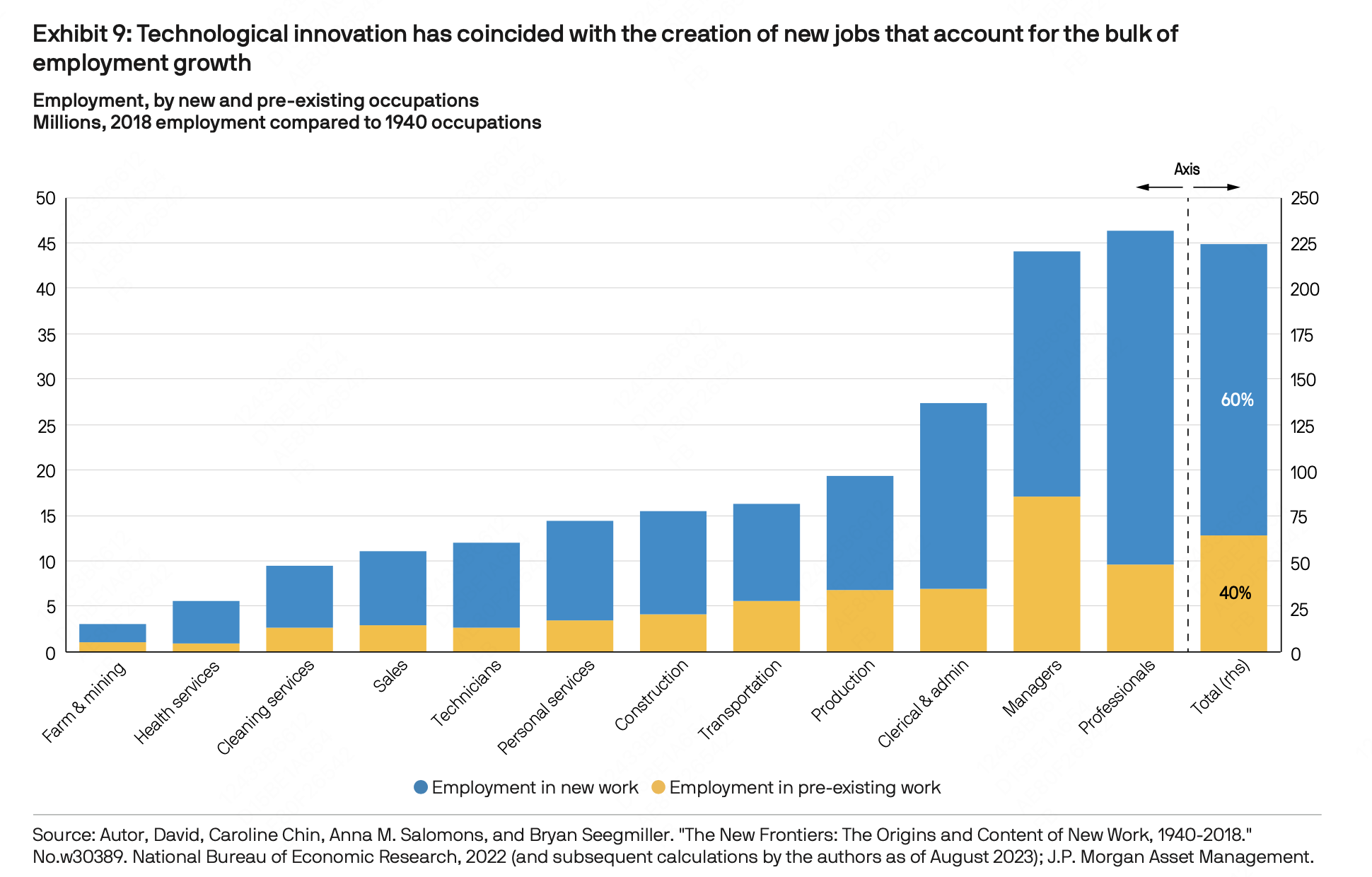
- Automation and Innovation: A substantial portion of AI’s impact will come from automating tasks currently performed by humans, which can help offset the effects of an aging workforce. Moreover, AI’s role in spurring innovation could amplify productivity gains.
- Labor Market Shifts: AI’s introduction will likely lead to transitional job displacement, wage adjustments, and potential increases in income inequality. However, job creation and overall economic growth driven by AI demand could mitigate these effects.
- Changing Workplace Dynamics: AI will alter the nature of value creation in the workplace, emphasizing skills where humans hold comparative advantages. Rapid and unpredictable changes will heighten the need for career flexibility and re-training.
- Market Implications: AI-driven productivity gains are expected to be favorable for corporate earnings and equity returns. The impact on bond markets is less clear but is anticipated to result in modestly higher yields.
Recommendations:
- Embracing AI for Economic Growth: Stakeholders should recognize and leverage AI’s potential to stimulate economic growth and innovation.
- Preparing for Labor Market Transformations: Businesses and governments need to prepare for shifts in the labor market by fostering career flexibility and investing in re-training programs.
- Policy Development: Effective policy action is crucial to manage AI’s impact on income inequality and job displacement.
- Skill Development Focus: Emphasis should be placed on developing skills where humans excel over AI, particularly in creative and interpersonal domains.
- Investment in AI Technologies: Continued investment in AI research and development is recommended to sustain its positive impacts on productivity and market growth.
Thinking Critically
Implications:
- Economic Disruption and Growth: If organizations and governments effectively adopt AI, particularly generative AI, we could witness a significant boost in economic growth, mirroring the transformative impacts of the steam engine and computers. This would entail not just an increase in productivity but also a potential upsurge in new industries and job categories. Conversely, failure to adopt or adapt to AI could widen the technological and economic gap between early adopters and laggards, possibly exacerbating global economic inequalities.
- Labor Market Transformation: The widespread adoption of AI is likely to lead to significant labor market shifts, with automation replacing some jobs while creating new ones. If managed well, this transition could lead to a more efficient, innovative workforce. However, without adequate policies and re-training programs, there could be heightened risks of unemployment, income inequality, and social unrest.
- Policy and Ethical Challenges: The report’s findings suggest a need for proactive policy development to address the challenges posed by AI, such as privacy concerns, ethical use of technology, and income inequality. This necessitates a collaborative approach among governments, corporations, and other stakeholders to ensure that the benefits of AI are equitably distributed and its risks are mitigated.
Alternative Perspectives:
- Overestimation of AI Capabilities: Critics might argue that the report overestimates the ability of generative AI to drive economic growth and productivity. Skeptics could point out that AI, while powerful, still faces significant hurdles in areas like ethical decision-making, contextual understanding, and creative thinking, which might limit its transformative impact.
- Underestimation of Displacement Impact: The report might be underplaying the potential negative impacts of AI on the job market. There is a possibility that AI could lead to significant job displacement without an equivalent rate of job creation, particularly in certain sectors or regions, leading to economic and social challenges.
- Potential for Increased Inequality: While the report suggests AI could exacerbate income inequality, it might not fully account for the extent of this issue. The rapid adoption of AI could disproportionately benefit those with the skills or resources to leverage these technologies, widening the gap between the ‘tech-savvy’ and the ‘tech-lacking.’
AI Predictions:
- Increased Productivity and Economic Growth: Based on the report’s findings, it’s reasonable to predict that AI, especially generative AI, will play a significant role in boosting global productivity and economic growth over the next decade.
- Rise in AI-Driven Job Markets: We can expect a surge in new job categories and markets driven by AI innovations. These jobs will likely require new skill sets focused on AI management, ethical considerations, and human-AI collaboration.
- Policy and Ethical Framework Development: Given the transformative impact of AI outlined in the report, it is likely that the next few years will see a substantial increase in the development of policies and ethical frameworks governing AI use, focusing on privacy, data security, and equitable access.
Glossary
- General-Purpose Technology: A term used to describe technologies, like generative AI, that have broad applications and the potential to trigger significant economic and social transformations, similar to past technologies like the steam engine and computer.
- Labor Productivity Growth: Refers to the increase in output per labor hour, which is projected to accelerate due to the implementation of AI technologies.
- Transitional Job Displacement: The phenomenon where the introduction of AI in various sectors could temporarily displace existing jobs, necessitating workforce adaptation and re-training.
- Career Flexibility: The increasing importance for individuals to adapt to rapid and unpredictable changes in the job market, particularly in the context of AI-driven transformations.
- AI-Driven Productivity Gains: Economic benefits reflected in corporate earnings and equity returns, attributed to the increased efficiency and innovation brought about by AI technologies.
- Ethical Use of Technology: A concept emphasizing the need for responsible and morally sound application of AI, considering factors like privacy, data security, and societal impact.
- Equitable AI Distribution: The challenge of ensuring that the benefits of AI are shared broadly and do not exacerbate existing inequalities, particularly in the context of its economic and labor market impacts.
Members also get access to our comprehensive database of AI tools and fundraising


 Join hosts Anthony, Shane, and Francesca for essential insights on AI's impact on jobs, careers, and business. Stay ahead of the curve – listen now!
Join hosts Anthony, Shane, and Francesca for essential insights on AI's impact on jobs, careers, and business. Stay ahead of the curve – listen now!