- Publication: Cognizant
- Publication Date: January 10, 2024
- Organizations mentioned: IDC (International Data Corporation), Microsoft, OpenAI, Google, Embassy of Things
- Technical background required: Medium
- Estimated read time (original text): 27 minutes
- Sentiment score: 68%, Somewhat positive (100% being most positive)
Generative AI is transforming the manufacturing industry by offering solutions to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer experience. It provides real-time data analysis for contextual insights, evaluates designs rapidly, and serves as a co-pilot for operations and customer service, thereby boosting productivity and reducing errors.
TLDR
Goal:
This report by Cognizant explores the transformative potential of Generative AI in the manufacturing industry. It addresses the industry’s ongoing evolution towards improved efficiency, cost reduction, and enhanced customer experience, set against the backdrop of increasing customer expectations, market fluctuations, and the need for sustainable practices.
Methodology:
- The methodology includes a deep understanding of gen AI capabilities, entailing problem definition, applicability assessment, data preprocessing, algorithm selection, and scaling to business functions.
- It compared and analyzed different gen AI models and their applications in the manufacturing industry.
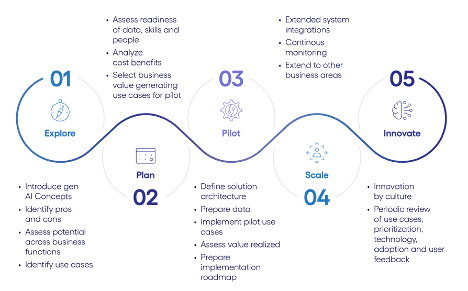
- The approach emphasizes identifying specific functions and use cases benefiting from gen AI and prioritizing these for pilot projects before wider implementation.
Key Findings:
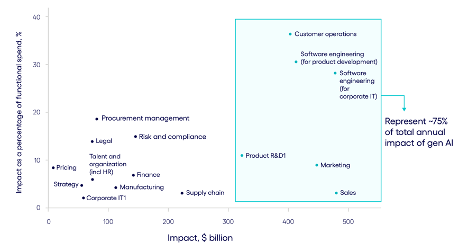
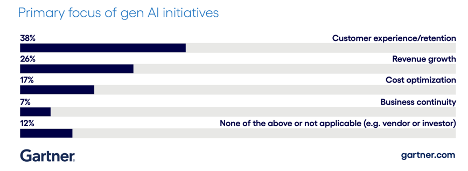
- Gen AI significantly boosts productivity and user experience in manufacturing, particularly in after-sales operations, product development, marketing, and sales.
- Analysts predict these areas, including customer operations and software engineering, could represent 75% of gen AI’s total annual value.
- Gen AI’s effectiveness lies in generating new data instances, with large language models enabling it to understand and generate human-like responses.
- Identified use cases for gen AI in manufacturing are categorized into conversational, referential, and creative applications.
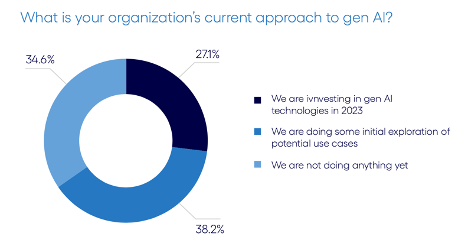
- 27% of companies in the manufacturing industry are actively investing in gen AI technology, expecting significant impacts on operational costs and efficiency.
Recommendations:
- Organizations should thoroughly understand gen AI’s capabilities and assess its benefits for their specific business needs.
- Identifying and prioritizing use cases for gen AI is crucial, with a focus on enhancing customer experience or reducing costs.
- The adoption of gen AI should be an iterative process, continuously expanded based on key success metrics.
- Decisions on gen AI use should include choosing appropriate technology providers and assessing data readiness and required expertise.
- Consideration of the human impact is vital, including workforce upskilling, cross-skilling, and attention to governance, security, and compliance issues.
Thinking critically
Implications:
- Gen AI could significantly enhance manufacturing productivity, leading to faster innovation, reduced operational costs, and improved customer experience.
- Companies that do not adopt gen AI may face higher operational costs, slower innovation cycles, and potential market share loss to competitors who leverage gen AI for efficiency and customer experience enhancements.
- The widespread adoption of gen AI in manufacturing could have broader economic and social implications, including the creation of new job categories, a shift in workforce dynamics requiring reskilling and upskilling, and potential ethical, privacy, and bias concerns.
Alternative Perspectives:
- The report’s findings are based on current gen AI capabilities and market trends. The actual impact of gen AI could be limited by technological constraints, unforeseen economic factors, or societal resistance to rapid automation.
- The report advocates for cautious and ethical use of gen AI, but there may be inherent challenges in ensuring data privacy and mitigating biases in AI models.
- While gen AI creates new job opportunities, there is a risk of displacement for workers whose roles might become obsolete.
AI Predictions:
- As gen AI becomes integral to manufacturing, there will be a significant shift in workforce skills, with an emphasis on AI literacy, data analysis, and digital competencies.
- Gen AI will lead to a new level of automation in manufacturing, improving efficiency, reducing error rates, and enabling more personalized and flexible production capabilities.
- There will be an increased focus on developing robust ethical guidelines and governance structures to manage AI’s impact on data privacy, bias, and workforce dynamics.
Glossary
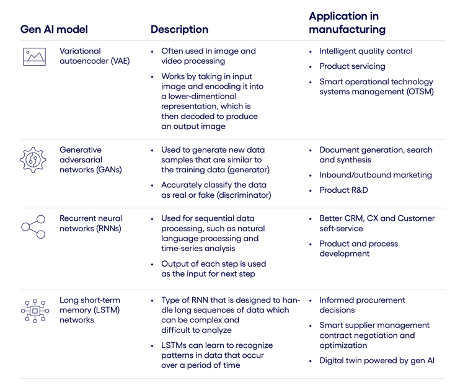
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): A type of AI algorithm that generates new data resembling its training set.
- Variational Autoencoders (VAEs): AI algorithms that learn data patterns to generate new data points.
- Chain-of-Thought (CoT) Activities: A gen AI function involving processes that simulate human-like thought sequences.
- Data Point Generation: Gen AI’s capability to create new instances of data that mimic its training dataset.
- Content Generation: Gen AI tools can produce new content with minimal or no human guidance.
- Content Summarization: These tools can summarize existing content in an easily understandable format for specific audiences.
- Intelligent Conversations: Gen AI can engage in human-like conversations across various domains.



 Join hosts Anthony, Shane, and Francesca for essential insights on AI's impact on jobs, careers, and business. Stay ahead of the curve – listen now!
Join hosts Anthony, Shane, and Francesca for essential insights on AI's impact on jobs, careers, and business. Stay ahead of the curve – listen now!