- Publication: JP Morgan
- Publication Date: 2023
- Organizations mentioned: OpenAI, Google, McKinsey & Company, U.S. Department of Agriculture, IBM
- Publication Authors: Michael Albrecht, Stephanie Aliaga
- Technical background required: Medium
- Estimated read time (original text): 60 minutes
- Sentiment score: 70%, Somewhat positive
The report, titled “The Transformative Power of Generative AI,” explores the profound potential of generative AI to revolutionize various domains, including work, innovation, and creation. It emphasizes generative AI’s versatility and intuitive nature and discusses its potential to become a general-purpose technology, transforming the global economy.
TLDR
Goal: The report aims to understand how AI is transforming market and consumer insights within large organizations. It seeks to provide a current snapshot of AI’s role in the industry and predict future trends, influenced by the growing importance of AI in data analysis and decision-making processes.
Methodology:
- The analysis employs a qualitative review of current generative AI technologies and their applications.
- It includes case studies and expert opinions to evaluate the influence of AI in different sectors.
- The analysis utilizes the O*NET task dataset, combined with U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) data, to estimate the potential impact of AI automation on various job tasks.
Key Findings:
- Generative AI has the potential to increase global productivity by up to 3% annually, revolutionizing work and innovation.
- Significant advancements are noted in fields like healthcare, where AI aids in decision-making and diagnoses.
- AI’s impact on the job market is twofold: it creates new opportunities while also posing challenges for workforce adaptation.
- Ethical considerations and data privacy emerge as critical concerns in the deployment of AI technologies.
- Collaboration between the public and private sectors is vital for maximizing AI benefits and mitigating risks.
Recommendations:
- Ongoing research and development in AI technologies are essential for sustaining innovation and effectively addressing the challenges that arise.
- Workforce retraining and upskilling are critical to align with the evolving job market influenced by AI advancements.
- Establishing ethical guidelines and robust data privacy policies is crucial in the implementation of AI technologies.
- Cross-industry collaboration can leverage AI for widespread economic and societal benefits.
- Government involvement in AI regulation is necessary to ensure equitable and safe development across various sectors.
Thinking Critically
Implications:
- The shift towards task automation by AI has the potential to enhance job roles’ efficiency and productivity, emphasizing the need for skill development and training.
- Different job types will experience varying impacts from AI, potentially altering labor market dynamics and increasing the value of human-centric skills.
- Widespread AI adoption could stimulate economic growth and innovation, but non-adoption might lead to competitive disadvantages. Moreover, this transition may influence equity markets, potentially increasing yields as AI-driven productivity boosts economic activity and reshapes financial sectors.
Alternative Perspectives:
- The optimistic outlook on AI’s capability to augment jobs might underestimate the potential negative impacts on employment, particularly in sectors where AI can perform tasks more efficiently than humans.
- The assumption that all workforce segments can adapt or be retrained for new roles overlooks potential challenges in skills mismatch and the economic feasibility of such large-scale training.
- The belief in AI as a major driver of future economic growth may not fully account for the complexities and uncertainties in AI development and its societal acceptance.
AI Predictions:
- There will likely be a rise in new job roles that synergize human skills with AI capabilities, particularly in sectors like healthcare, finance, and customer service.
- AI’s impact on automating tasks will drive a significant transformation in educational and training programs, emphasizing skills where humans excel over AI.
- Public and private sectors will likely increase collaboration to harness AI’s benefits while addressing challenges like data privacy and workforce transitions.
Glossary
- Generative AI: AI technologies capable of producing new, unique content or solutions by understanding and processing existing information.
- LLMs (Large Language Models): AI models, like those developed by OpenAI, proficient in understanding and generating human language.
- Automation: The use of technology to perform tasks without human intervention, often to increase efficiency and reduce error.
- AI Augmentation: The concept where AI enhances human capabilities in a job rather than completely replacing them.
- Chatbots: Automated software applications that use AI to simulate human conversation, often used in customer service and informational queries.
- Robo-advisers: Automated platforms providing financial advice and portfolio management using algorithms, complemented by human advisers for complex tasks.


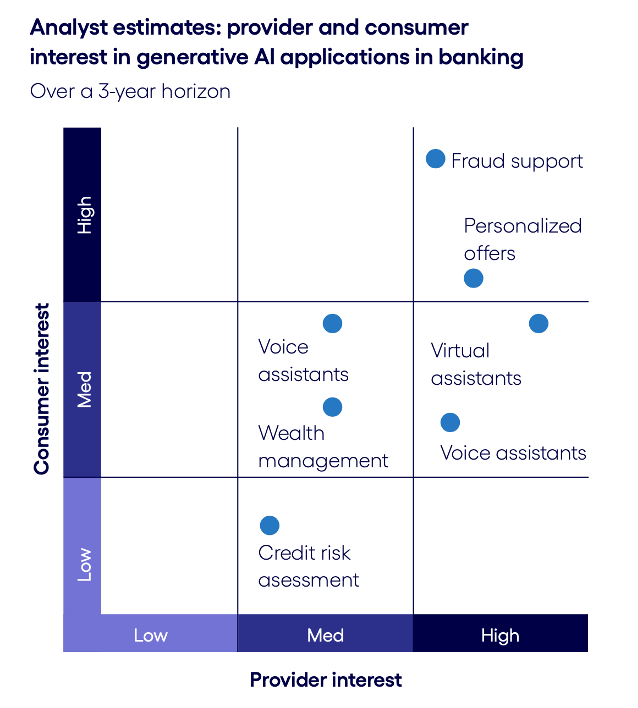
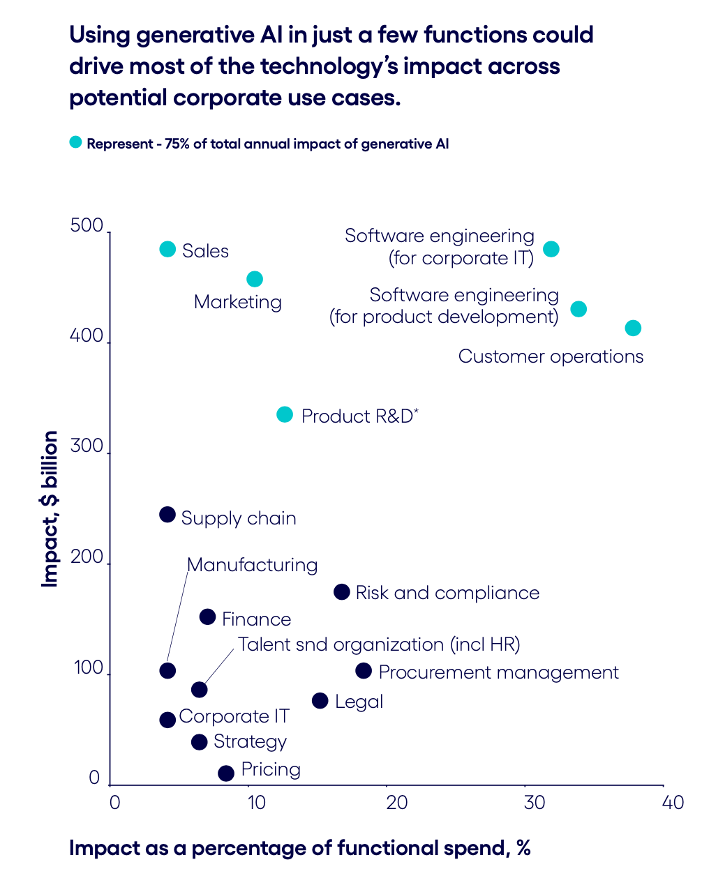
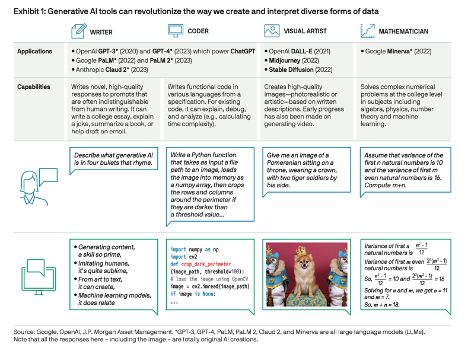
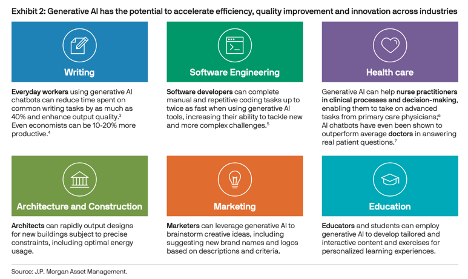
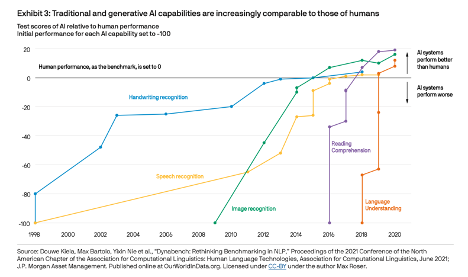
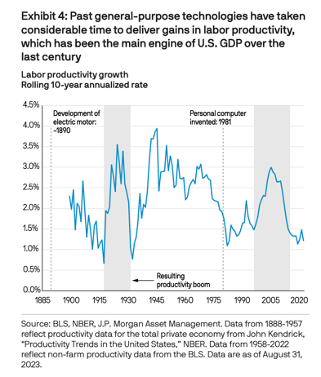

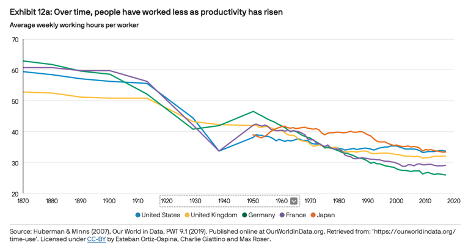
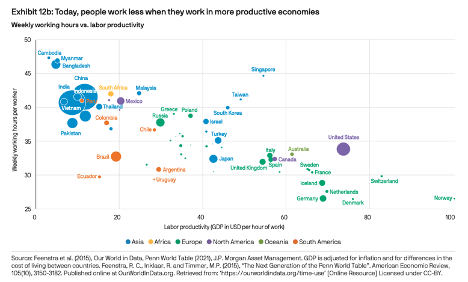
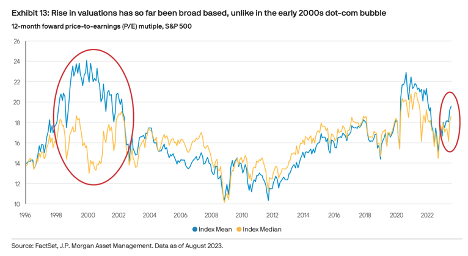
 Join hosts Anthony, Shane, and Francesca for essential insights on AI's impact on jobs, careers, and business. Stay ahead of the curve – listen now!
Join hosts Anthony, Shane, and Francesca for essential insights on AI's impact on jobs, careers, and business. Stay ahead of the curve – listen now!