- Publication: pwc
- Publication Date: May, 2017
- Organizations mentioned: pwc
- Publication Authors: Dr. Anand S. Rao and Gerard Verweij
- Technical background required: Medium
- Estimated read time (original text): 60 minutes
- Sentiment score: 70%, Somewhat positive
Goal:
The report aims to assess the economic potential of AI by 2030, identifying key sectors and regions that stand to benefit the most from AI adoption.
Methodology:
- AI Impact Index: Evaluates nearly 300 use cases to assess the potential impact of AI on personalization, quality, and time-saving aspects.
- Economic Analysis: Utilizes machine learning and econometrics to quantify the impact of AI on productivity, job automation, and consumer utility.
Key findings:
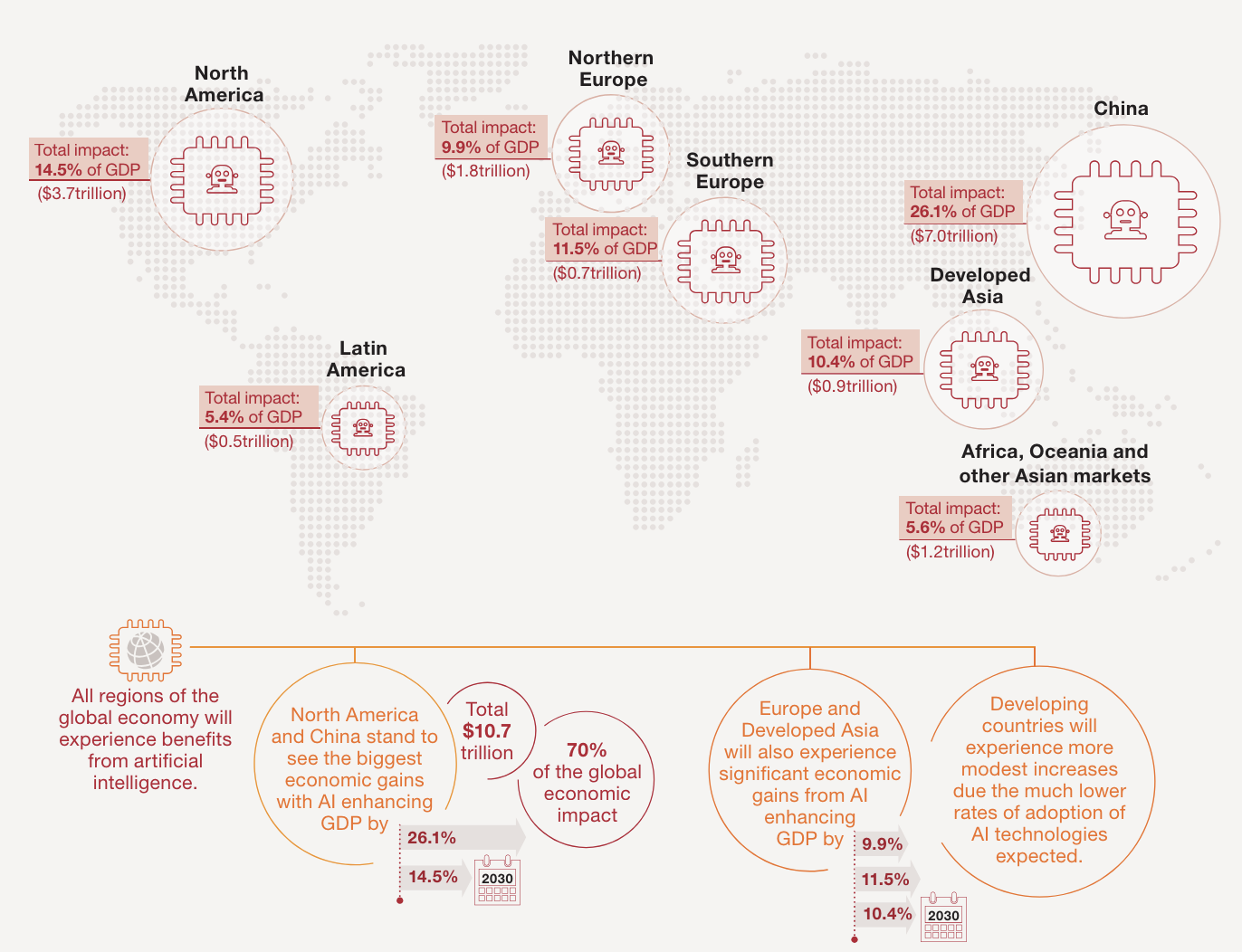
- Global GDP could increase by up to 14% in 2030, with AI contributing $15.7 trillion to the economy.
- AI has the potential to enhance productivity, quality, and personalization across sectors like healthcare, automotive, and financial services.
- China and North America are projected to see substantial GDP boosts of up to 26% and 14%, respectively.
- The biggest gains from AI are expected in sectors like retail, financial services, and healthcare due to increased productivity and product quality.
Recommendations:
- Prioritize response to AI disruption by identifying opportunities and building necessary talent and technology capabilities.
- Establish a data-driven culture to blend intuition with analytical insights and make practical decisions.
- Build trust and transparency into AI platforms to address ethical implications and ensure regulatory acceptance.
- Prepare for a hybrid workforce where AI and humans work collaboratively, and invest in training for emerging tech roles.
Implications:
- Adoption of the recommendations in this report could lead to a significant increase in global GDP by up to 14% in 2030, equivalent to an additional $15.7 trillion. This would make AI the biggest commercial opportunity in the fast-changing economy, benefiting sectors like retail, financial services, and healthcare.
- Countries like China and North America stand to gain the most from AI, with potential GDP boosts of up to 26% and 14% respectively by 2030. Emerging markets could leapfrog ahead of developed counterparts with AI adoption.
- The potential for job displacement due to AI adoption is a concern, but new employment opportunities will also be created as businesses adopt AI technologies, requiring a workforce with new skills and expertise.
Alternative Perspectives:
- Some may argue that the methodology used in the report to estimate the impact and potential of AI, such as the AI Impact Index and economic analysis approach, could be flawed or based on inconsistent assumptions. This could lead to overestimation of the potential benefits of AI.
- Critics may point out that the reliance on AI for productivity gains and economic growth could lead to increased inequality and job insecurity, as automation disrupts traditional job roles and creates a divide between those with AI skills and those without.
- Others may predict that the pace of AI adoption and the actual economic impact could be slower than projected, as businesses face challenges in integrating AI technologies, addressing regulatory concerns, and building trust in AI systems.
AI Predictions:
- Modest predictions suggest that AI adoption will continue to grow steadily, with industries like healthcare, automotive, and financial services leading the way in leveraging AI for productivity gains and consumer benefits.
- AI technologies such as deep learning, natural language processing, and robotic process automation will play a significant role in transforming business processes and customer interactions in the near future.
- As AI becomes more mainstream and integrated into daily operations, businesses will need to focus on building a data-driven culture, investing in talent development, and implementing robust governance and control mechanisms to ensure responsible and transparent AI use.
Glossary
- Sizing the Prize: The concept of evaluating the economic potential of AI and its impact on global GDP.
- Human in the Loop: The idea of humans and machines collaborating closely in AI applications.
- Hardwired Systems: AI systems that do not learn from their interactions.
- Adaptive Systems: AI systems that can adapt to different situations and act autonomously.
- Assisted Intelligence: AI systems that assist humans in making decisions or taking actions.
- Augmented Intelligence: AI systems that augment human decision-making and continuously learn from their interactions.
- Automation: The automation of manual and cognitive tasks, either routine or non-routine.
- No Human in the Loop: The concept of AI systems that can operate autonomously without human assistance.
- Autonomous Intelligence: AI systems that act autonomously without human intervention.
Members also get access to our comprehensive database of AI tools and fundraising


 Join hosts Anthony, Shane, and Francesca for essential insights on AI's impact on jobs, careers, and business. Stay ahead of the curve – listen now!
Join hosts Anthony, Shane, and Francesca for essential insights on AI's impact on jobs, careers, and business. Stay ahead of the curve – listen now!