- Publication: Accenture
- Publication Date: 2023
- Organizations mentioned: The Washington Post, The New York Times, Intel, Mizuho Financial Group, NVIDIA
- Publication Authors: Ellyn Shook, Paul Daugherty
- Technical background required: Low
- Estimated read time (original text): 60 minutes
- Sentiment score: 75%, Somewhat positive
TLDR
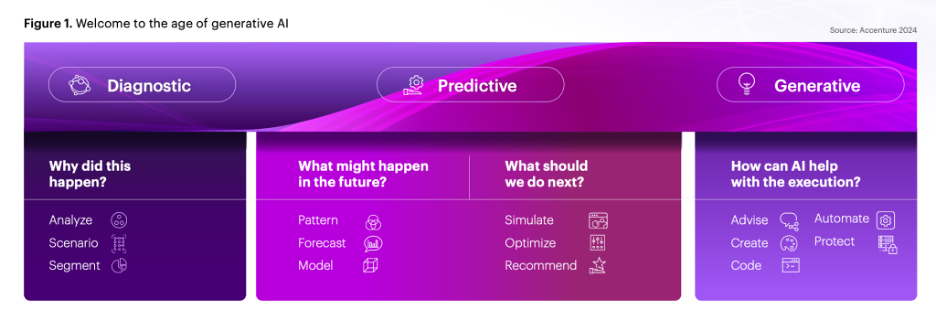
Goal: The report aims to explore the transformative impact of generative AI on work, the workforce, and workers. It delves into the changes that generative AI is bringing to various industries, emphasizing its potential to revolutionize not just productivity but also human creativity and innovation in the workplace.
Methodology:
- The study employs three scenarios to model generative AI adoption: aggressive, cautious, and people-centric, using GDP growth projections for 22 countries as a baseline.
- Analysis of automation and augmentation impacts of generative AI on language-based job tasks was conducted using data from O*NET, US Bureau of Labor Statistics, and others, combined with machine learning to predict job transitions and quality assessments.
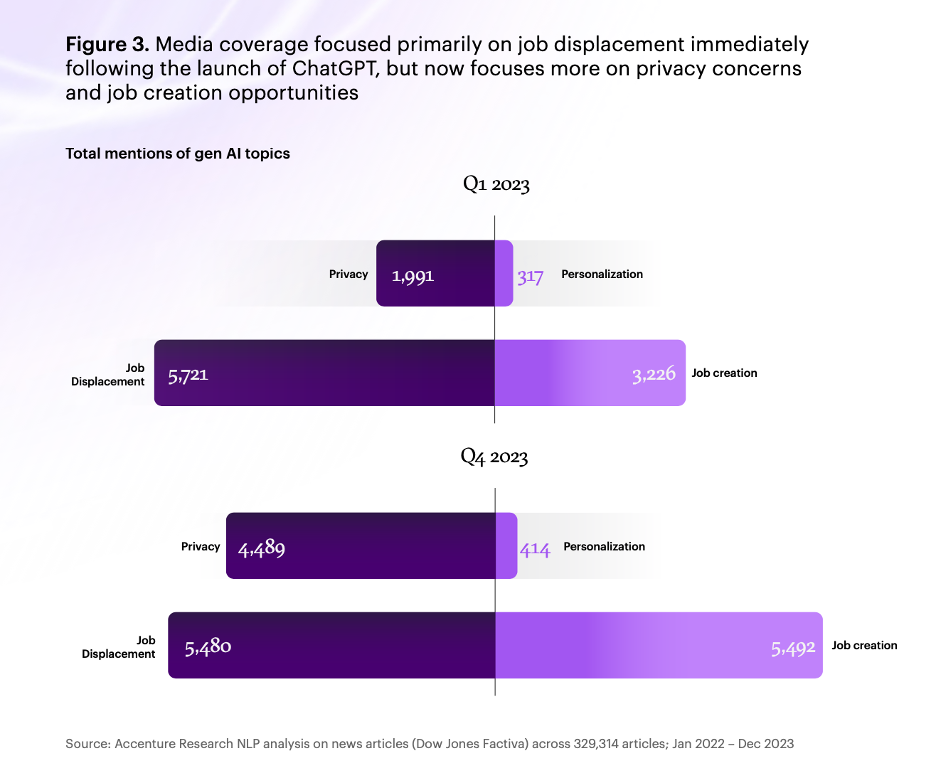
- The report includes a media sentiment analysis of over 300,000 articles, using semantic text analysis and Natural Language Processing to track evolving discussions and perceptions about generative AI and Large Language Models (LLMs).
Key Findings:
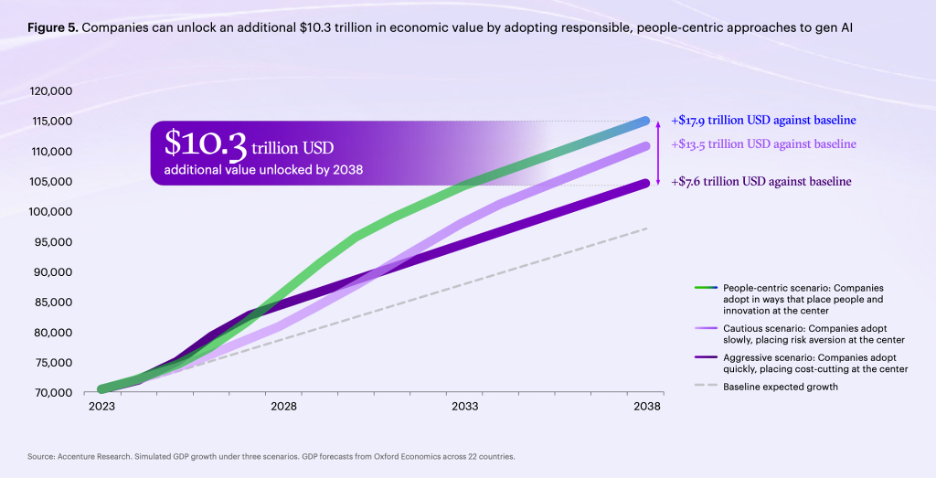
- Economic Impact: Generative AI could unlock more than $10.3 trillion in additional economic value by 2038, with productivity gains of 20% or more in the next three years. CxOs are optimistic about AI increasing their company’s market share.
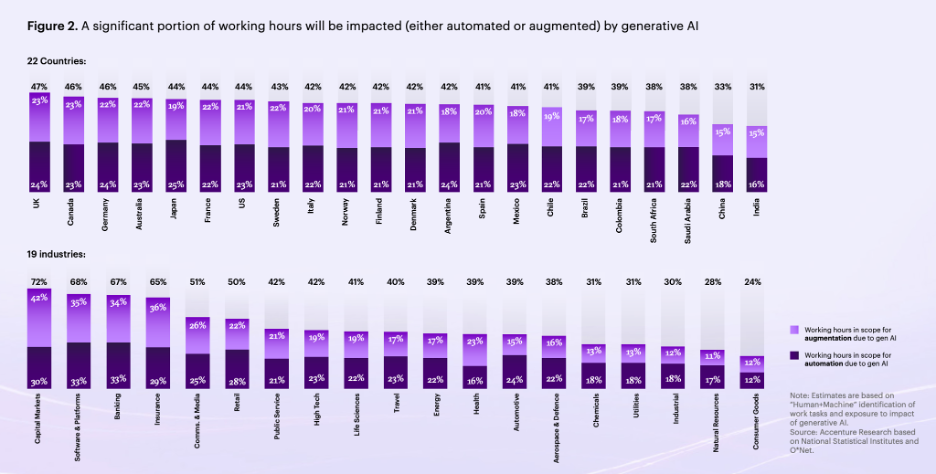
- Workforce Transformation: 44% of working hours in the US (higher in other countries) are in scope for automation or augmentation by generative AI. This shift highlights the potential for exacerbating the digital divide and the need for reskilling the workforce.
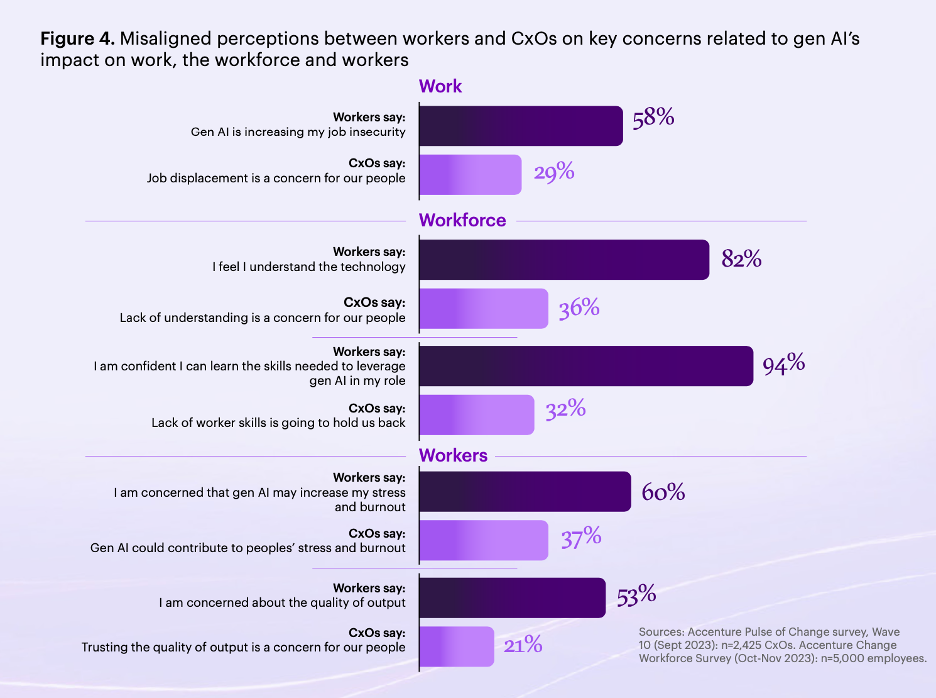
- Trust Gap and Employee Sentiment: There exists a significant trust gap between workers and leaders regarding the integration and outcomes of AI. Employees express concerns about job security, stress, and burnout, while leaders often underestimate these concerns.
- Reinventors Leading the Way: A small percentage of organizations, termed ‘Reinventors’, are at the forefront of leveraging generative AI effectively. They focus on continuous reinvention, integrating AI into business processes, and involving employees in change efforts.
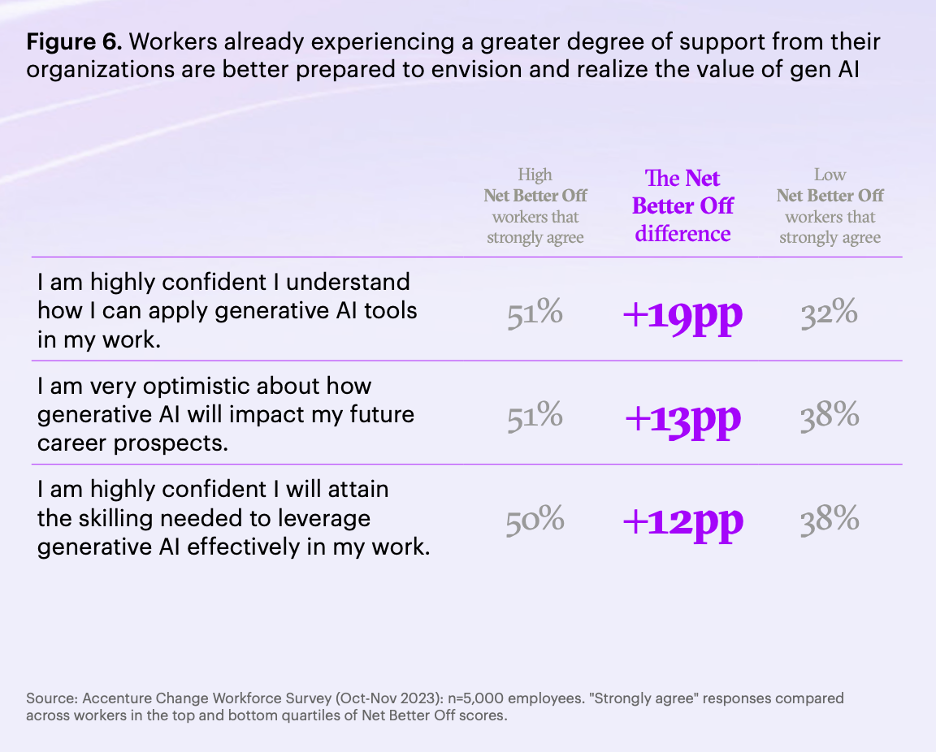
- Net Better Off Approach: Accenture’s research suggests that helping employees feel ‘Net Better Off’ in terms of emotional, physical, and financial well-being can unlock their potential, leading to a 5% revenue boost.
- Leadership and Learning: Effective leadership in the age of generative AI requires a new approach to learning and decision-making. Leaders must be adept at understanding and navigating the complexities of AI integration and fostering a culture of trust and transparency.
Recommendations:
- Organizations should focus on human-centered change efforts to ensure that AI implementation benefits both the business and its employees.
- To prepare the workforce for the AI era, significant investment in reskilling programs is necessary, focusing on both technological and soft skills.
- Building trust in AI technologies requires transparent communication and involving employees in AI implementation strategies.
- Organizations should prioritize a people-centric approach in adopting AI, ensuring that it enhances rather than replaces human work.
- Leaders must actively engage with AI technologies and lead with compassion and humility, fostering an environment that encourages continuous learning and adaptation.
Thinking Critically
Implications:
- Widespread adoption of generative AI could lead to significant economic growth and productivity gains. However, this could also exacerbate the digital divide and lead to increased unemployment or underemployment in sectors heavily impacted by automation.
- Businesses that adopt a people-centric approach to AI will likely thrive, leading to a competitive advantage. This implies that companies ignoring these strategies might struggle to keep up with market demands and face challenges in employee engagement and innovation.
- The ethical implications of generative AI’s integration into workplaces raise concerns about privacy, job security, and the potential misuse of AI technologies. Organizations that proactively address these concerns will be better positioned to build trust with their stakeholders. Conversely, ignoring these aspects could lead to public backlash, legal challenges, and a loss of employee and consumer trust.
Alternative Perspectives:
- The methodology may oversimplify the complex dynamics of AI’s impact on the workforce. This could lead to underestimating the nuanced effects of AI across different sectors and job types, potentially overlooking unique challenges and opportunities in specific industries.
- The report’s focus on economic growth and productivity might overshadow the human aspect of AI integration, such as worker well-being and job satisfaction.
- The predictive models used to gauge job transitions and the quality of these transitions might not fully account for the unpredictable nature of technological advancements and human adaptation.
AI Predictions:
- There will likely be a growing demand for reskilling programs, particularly in industries heavily impacted by AI. This could lead to a surge in online learning platforms and corporate training programs focused on digital skills.
- The adoption of AI in various sectors will likely create new job roles that focus on AI management, ethics, and integration. These roles will be critical in bridging the gap between AI capabilities and human-centric business operations.
- Businesses may increasingly shift towards models that integrate AI not just for efficiency but also for enhancing human creativity and decision-making, leading to more innovative and adaptable business strategies.
Glossary
- Net Better Off Framework: A concept that assesses the impact of AI on employees’ well-being, including emotional, physical, and financial aspects, to enhance their overall work experience.
- Reinventors: A term used to describe organizations that are leading in the effective adoption and integration of generative AI into their business processes and employee engagement strategies.
- Aggressive Scenario: A generative AI adoption model characterized by a focus on cost-cutting, rapid adoption, and high rates of talent displacement, leading to increased unemployment.
- Cautious Scenario: An adoption approach where organizations slowly and cautiously implement generative AI, aiming to avoid talent displacement but lacking a focus on creating people-centric environments.
- People-Centric Scenario: A model of AI adoption that emphasizes augmenting work with generative AI while also creating supportive, people-centric environments to assist workers in adapting to changes.
- Trust Gap: The discrepancy between workers’ and leaders’ perceptions of AI integration and its outcomes, particularly concerning job security and work conditions.
- Occupational Information Network (O*NET): A database used in the report to analyze the impact of AI on job tasks, focusing on language-based tasks in various occupations and industries.
- Semantic Text Analysis: A method used in the report for analyzing media sentiment, involving the examination of language and context in over 300,000 media articles to understand perceptions of generative AI.
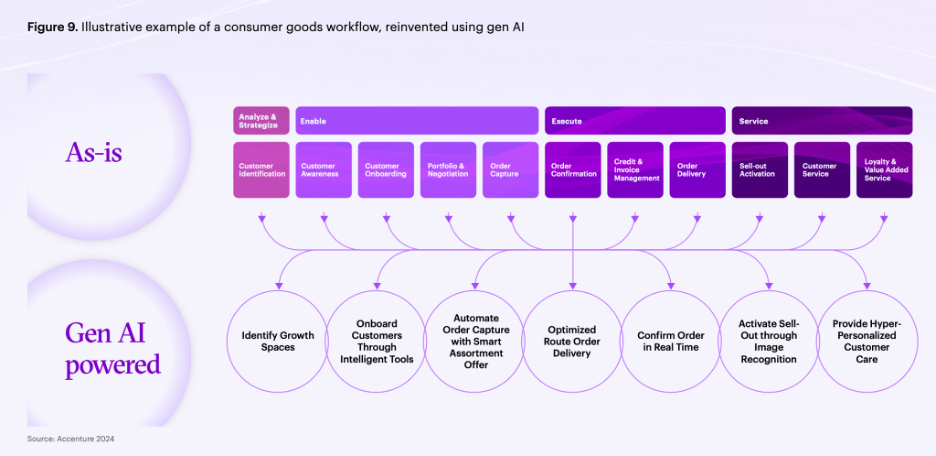
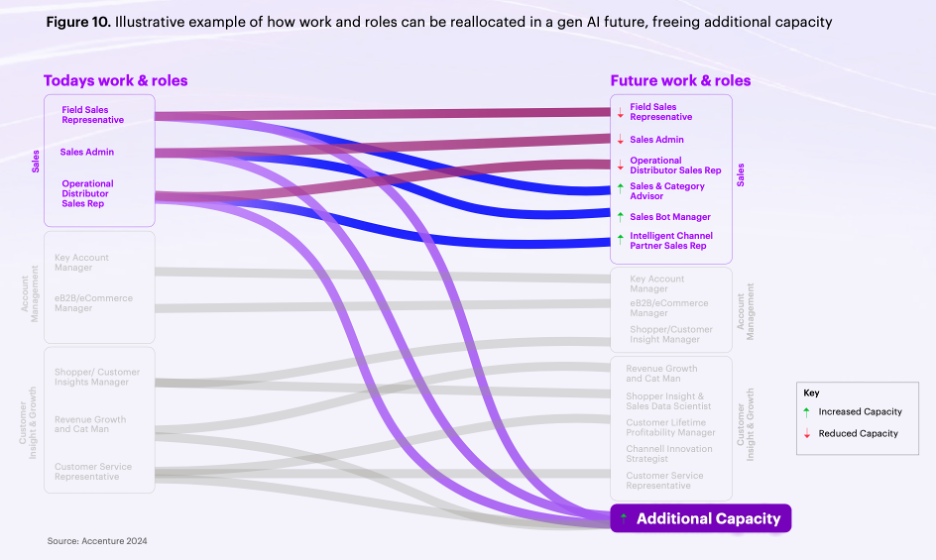
Figures
Members also get access to our comprehensive database of AI tools and fundraising




 Join hosts Anthony, Shane, and Francesca for essential insights on AI's impact on jobs, careers, and business. Stay ahead of the curve – listen now!
Join hosts Anthony, Shane, and Francesca for essential insights on AI's impact on jobs, careers, and business. Stay ahead of the curve – listen now!