- Publication: NBER (National Bureau of Economic Research)
- Publication Date: March 1, 2018
- Organizations mentioned: IBM, USPTO (United States Patent and Trademark Office), Atomwise, Thomson Reuters
- Publication Authors: Iain M. Cockburn, Rebecca Henderson, Scott Stern
- Technical background required: High
- Estimated read time (original text): 40 minutes (original text)
- Sentiment score: 60%, Neutral (100% being most positive)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has the potential to significantly increase the efficiency of the current economy and reshape the nature of the innovation process and the organization of R&D, with deep learning serving as a new general-purpose method of invention.
TLDR
Goal: The report, titled “The Impact of AI on Innovation,” primarily focuses on the transformative role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in reshaping the innovation process and the organization of Research and Development (R&D). It delves into how AI, particularly deep learning, is evolving from a tool for automation to a general-purpose method of invention. The study aims to provide insights into the economic and societal implications of these AI-driven changes, particularly how they influence productivity, employment, and competition.
Methodology:
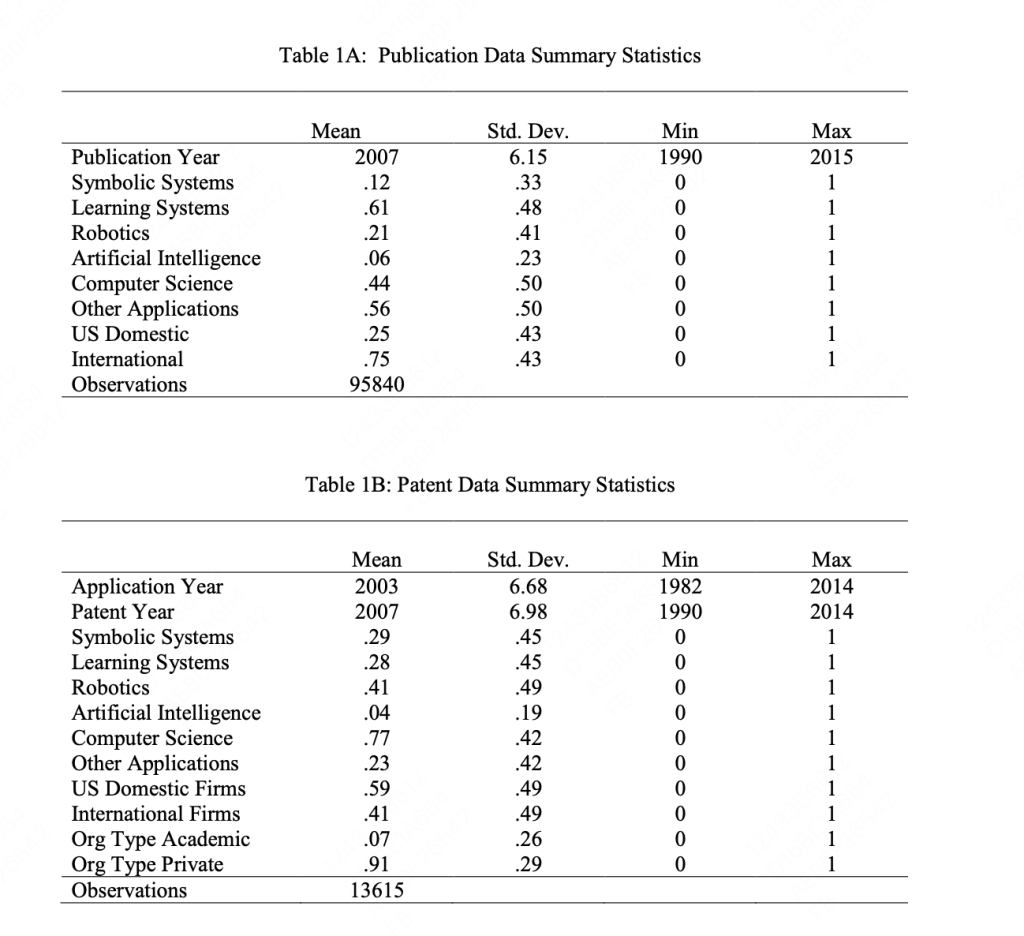
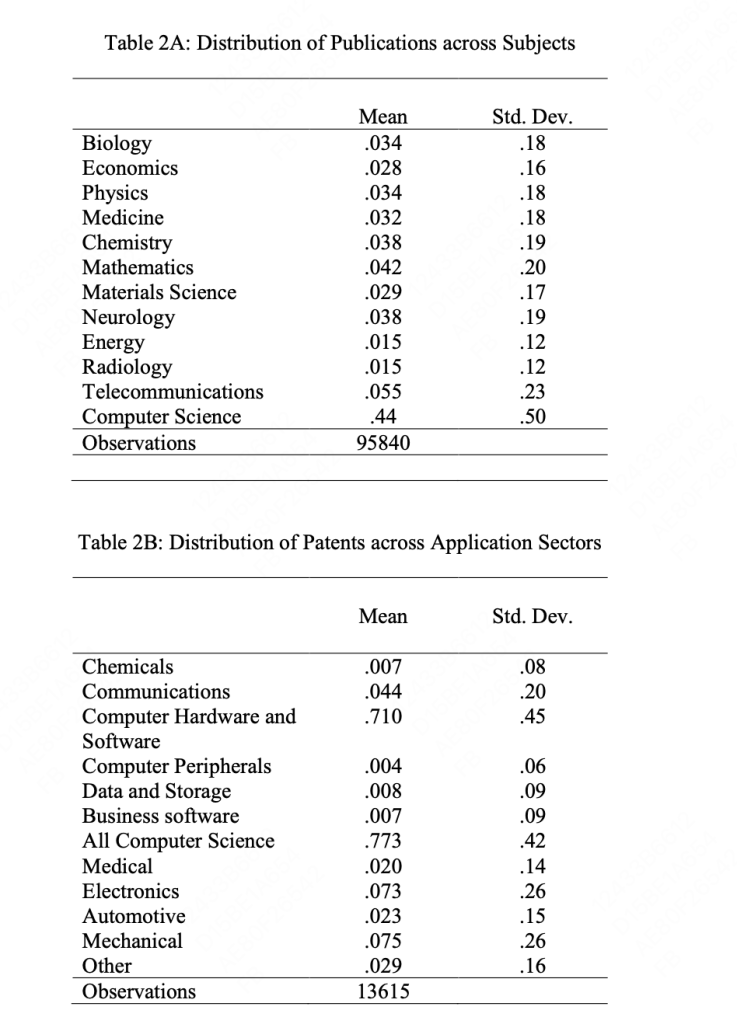
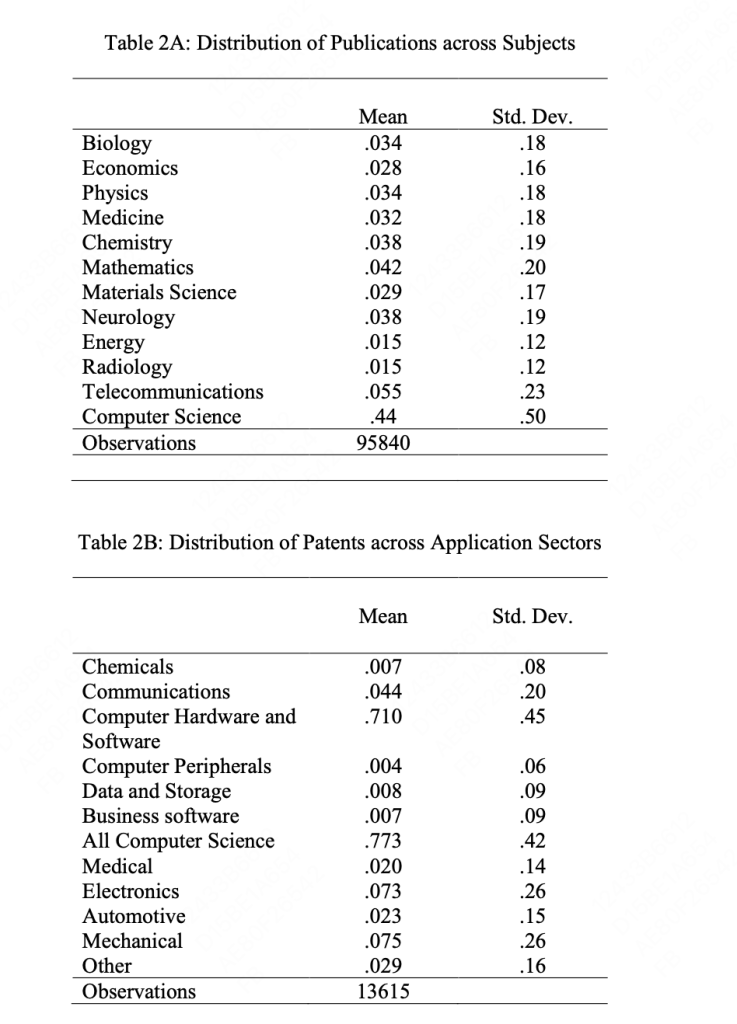
- The methodology involves an extensive analysis of AI’s evolution, emphasizing deep learning. This includes a bibliometric analysis of scientific papers and patents from 1990 through 2015, focusing on AI-related fields like robotics, symbolic systems, and deep learning.
- The study categorizes AI innovations and their application areas, analyzing trends and shifts in AI research and development, particularly the rapid rise in learning-oriented AI post-2009.
- The report uses a combination of qualitative and quantitative data, including publication and patent analysis, to identify trends in AI’s influence on different sectors and its potential as a General-Purpose Technology (GPT) and an Invention Method of Invention (IMI).
Key Findings:
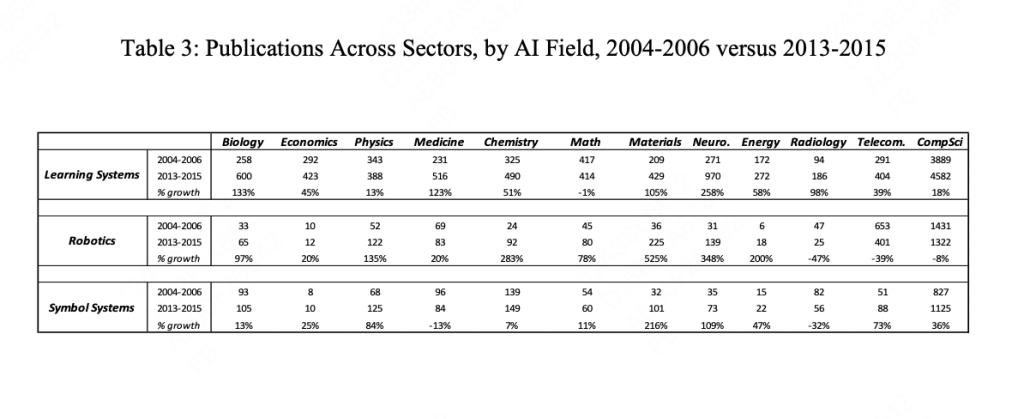
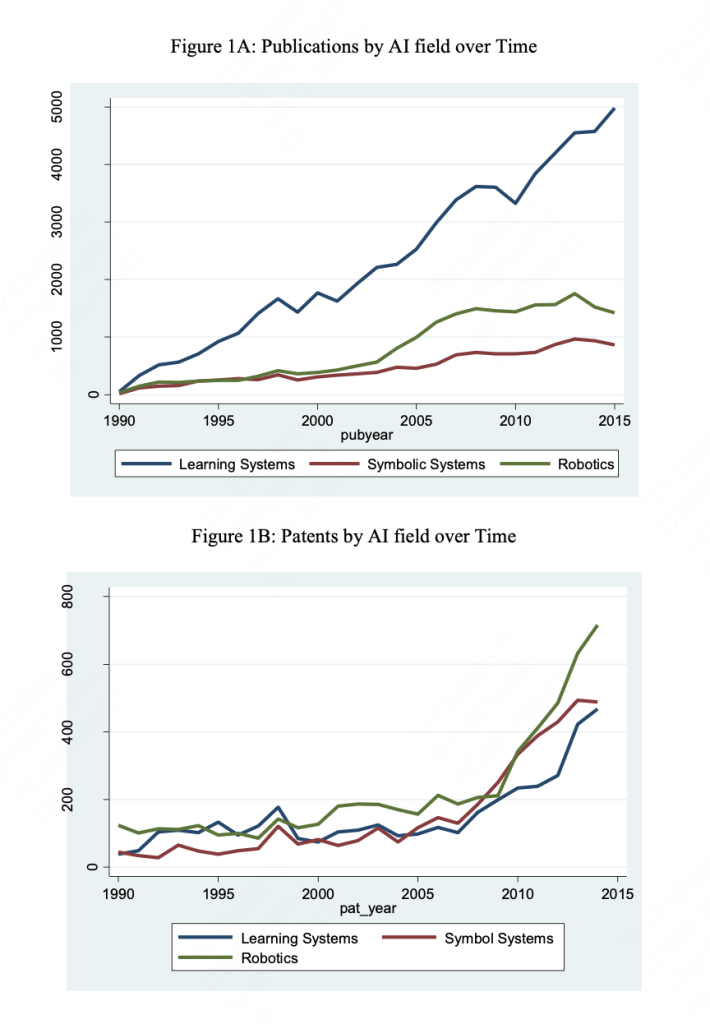
- Shift in AI Research Focus: There’s a notable shift towards learning-oriented AI research, especially in deep learning, since 2009. This shift suggests AI’s evolving role from specific applications to broader, more general-purpose uses.
- AI as a General-Purpose Technology: Deep learning, a key AI technology, is identified as a potential General-Purpose Technology (GPT). It’s characterized by its wide applicability across various fields, driving significant economic and technological advancements.
- Impact on the Innovation Process: AI, particularly deep learning, is not only enhancing the performance of technologies but also changing the nature of the innovation process itself, leading to more efficient and diverse research methods.
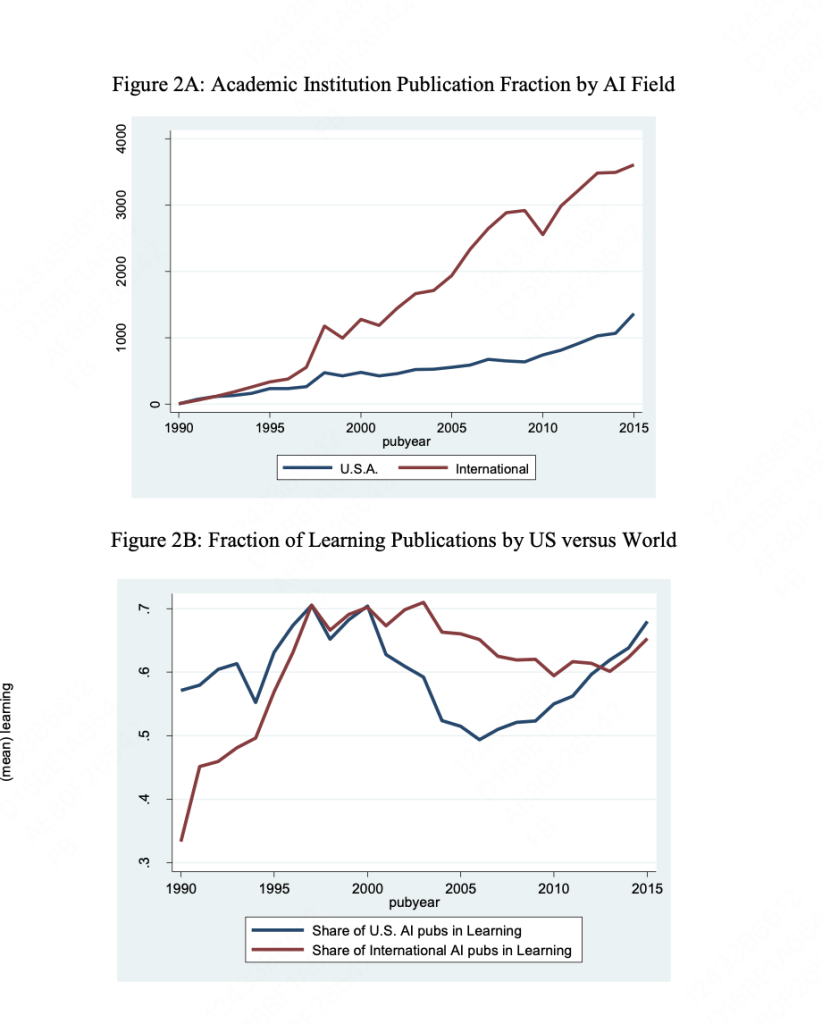
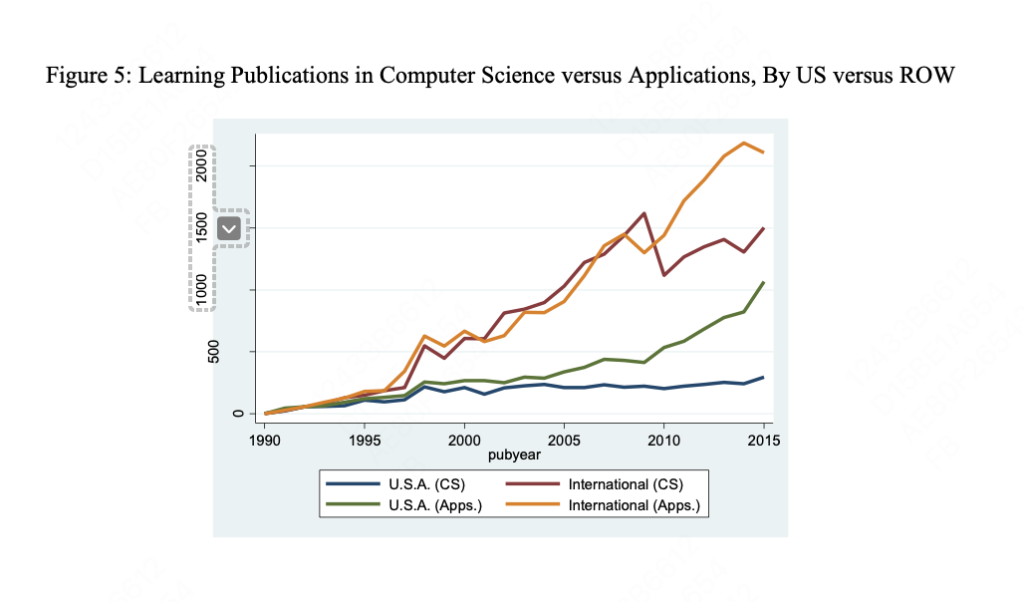
- Geographical Variations in AI Research: There are significant geographical differences in AI research, with the United States initially lagging in learning-oriented research but catching up post-2009.
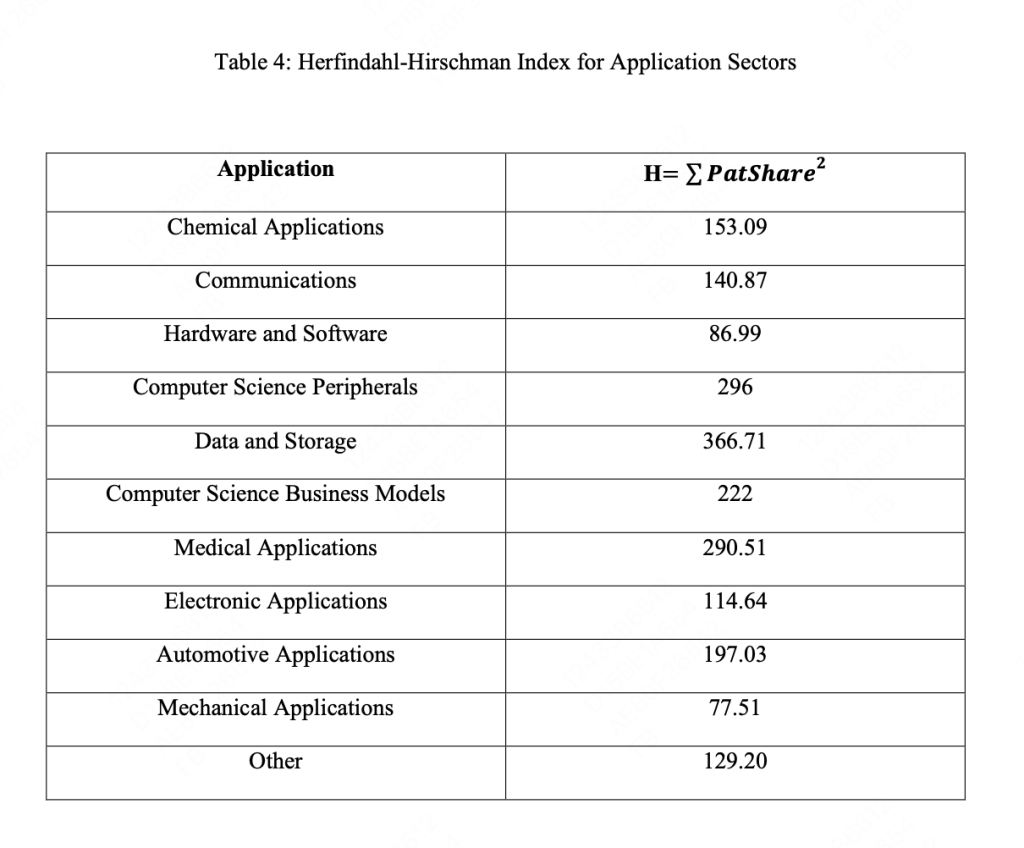
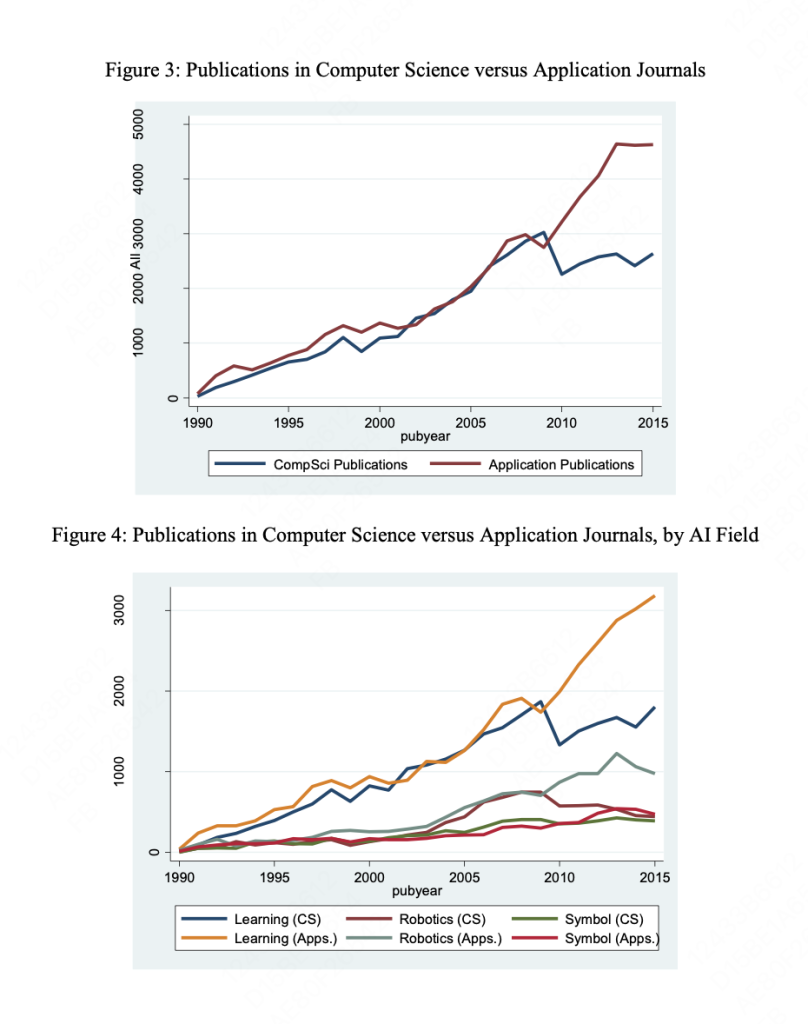
- Divergence in AI Fields: A divergence in AI research fields is observed, with robotics and symbolic systems having less impact on the innovation process compared to deep learning.
- Potential Economic and Societal Impacts: The report predicts that AI’s role as a GPT and IMI could lead to profound economic growth, outweighing its immediate impacts on job displacement and productivity.
Recommendations:
- Encourage Transparency and Data Sharing: Policies promoting transparency and sharing of core datasets across public and private sectors are crucial for stimulating research productivity and innovation-oriented competition.
- Focus on AI’s Predictive Analytics: Emphasis should be placed on harnessing AI’s predictive analytics capabilities to revolutionize scientific research and technical problem-solving.
- Address AI’s Economic and Social Impacts: It’s important to address the broad economic and societal impacts of AI, especially in terms of job displacement and the restructuring of industries.
- Support Diverse AI Application Areas: Supporting AI research across diverse fields, beyond traditional sectors, is vital for leveraging its full potential as a GPT.
- Develop Policies for Data Control and Competition: Policymakers should focus on developing regulations that manage the control of data critical to AI and ensure a competitive and fair AI-driven market.
Thinking Critically
Implications:
- Acceleration of AI-Driven Innovation: If organizations broadly adopt AI, especially deep learning, as a core tool for innovation, we can expect a rapid acceleration in technological advancements across various sectors. This could lead to significant increases in productivity and economic growth, as AI’s predictive analytics and data processing capabilities streamline and enhance the R&D process. Conversely, organizations that fail to integrate AI into their innovation strategies might fall behind, leading to a widened technological and competitive gap.
- Transformative Impact on Labor and Education: The report’s findings suggest a potential shift in labor dynamics, with a reduction in demand for routine, labor-intensive research roles and an increased need for skills in managing and interpreting AI-driven outputs. Educational institutions may need to adapt, focusing more on AI and data literacy. If organizations and educational systems fail to anticipate and adapt to these changes, there could be significant disruptions in the labor market and skill gaps.
- Policy and Ethical Considerations: The recommendation for transparent and shared data use in AI raises significant policy and ethical implications. Governments and international bodies may need to establish new frameworks to balance the benefits of data sharing with privacy and security concerns. The potential concentration of AI capabilities and data in a few dominant entities also raises questions about market monopolies and the need for antitrust regulations in the AI domain.
Alternative Perspectives:
- Questioning the Generalizability of AI as a GPT: While the report positions deep learning as a General-Purpose Technology, some may argue that its applicability and impact might be overestimated. The effectiveness of AI in certain sectors, especially those requiring nuanced understanding and creativity, could be less revolutionary than predicted, questioning the universal applicability of AI as a GPT.
- Economic Disruption and Job Displacement Risks: The optimistic view of AI’s impact on economic growth and innovation could be counterbalanced by concerns over job displacement and economic disruption. The rapid adoption of AI might lead to short-term unemployment and require substantial investments in retraining programs, a perspective not fully addressed in the report.
- Data Accessibility and Monopoly Concerns: The recommendation for data sharing and transparency might be overly optimistic, ignoring the potential reluctance of private entities to share proprietary data. This could lead to a concentration of AI capabilities in a few large corporations, exacerbating monopoly concerns and limiting the democratization of AI benefits.
AI Predictions:
- Widespread Adoption in Diverse Fields: Over the next decade, AI, particularly deep learning, will likely see widespread adoption across a broad range of industries, not just in technology sectors but also in areas like healthcare, agriculture, and finance, driving significant innovations.
- Shift in Research and Development Practices: AI will fundamentally change the nature of research and development. Organizations will increasingly rely on AI for predictive analysis and problem-solving, making traditional R&D methods less prevalent.
- Emergence of New AI Governance Frameworks: Given AI’s transformative impact, new governance frameworks and policies, particularly around data sharing and ethical AI use, will likely emerge, aiming to balance innovation with privacy, security, and equitable access.
Glossary
- General-Purpose Technology (GPT): A type of technology that has broad applicability across a wide range of sectors, driving significant economic and technological advancements.
- Invention Method of Invention (IMI): A concept that refers to innovations which fundamentally change the way new products or technologies are created, representing a new approach to innovation itself.
- Learning-oriented AI: A classification of AI research that focuses on the development and application of learning algorithms, particularly in the field of deep learning.
- Deep Learning: A subset of machine learning involving neural networks, characterized by its ability to process large sets of unstructured data and improve through experience, increasingly used as a tool for prediction and problem-solving across various sectors.
- Application-oriented Research: Research that is directed towards practical applications in specific fields, as opposed to theoretical or foundational research.
- AI-driven Output Management: The process of managing and interpreting the results produced by AI systems, particularly in the context of research and development.
- Predictive Analytics: The use of data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning techniques to identify the likelihood of future outcomes based on historical data.


 Join hosts Anthony, Shane, and Francesca for essential insights on AI's impact on jobs, careers, and business. Stay ahead of the curve – listen now!
Join hosts Anthony, Shane, and Francesca for essential insights on AI's impact on jobs, careers, and business. Stay ahead of the curve – listen now!