- Publication: BCG
- Publication Date: September 21, 2023
- Organizations mentioned: BCG Henderson Institute, Harvard Business School, MIT Sloan School of Management, Wharton School at the University of Pennsylvania, University of Warwick
- Publication Authors: François Candelon, Lisa Krayer, Saran Rajendran, and David Zuluaga Martínez.
- Technical background required: Low
- Estimated read time (original text): 20 minutes
- Sentiment score: 60%, Neutral
The report investigates how generative AI (GenAI) can both create and destroy value in professional settings. It focuses on the impact of GenAI on tasks like creative product innovation and business problem solving, revealing both positive and negative outcomes.
TLDR
Goal: The BCG report explores how generative AI (GenAI) influences professional tasks, specifically focusing on creative product innovation and business problem-solving. It seeks to understand how GenAI can enhance or diminish performance and the implications for diverse industries.
Methodology:
- A scientific experiment with over 750 Boston Consulting Group consultants as subjects.
- Participants were divided into groups to perform tasks with or without GenAI (OpenAI’s GPT-4), in areas like creative product innovation and business problem-solving.
- Performance was assessed based on task completion, with an emphasis on creativity, persuasive writing, and analytical thinking.
Key Findings:
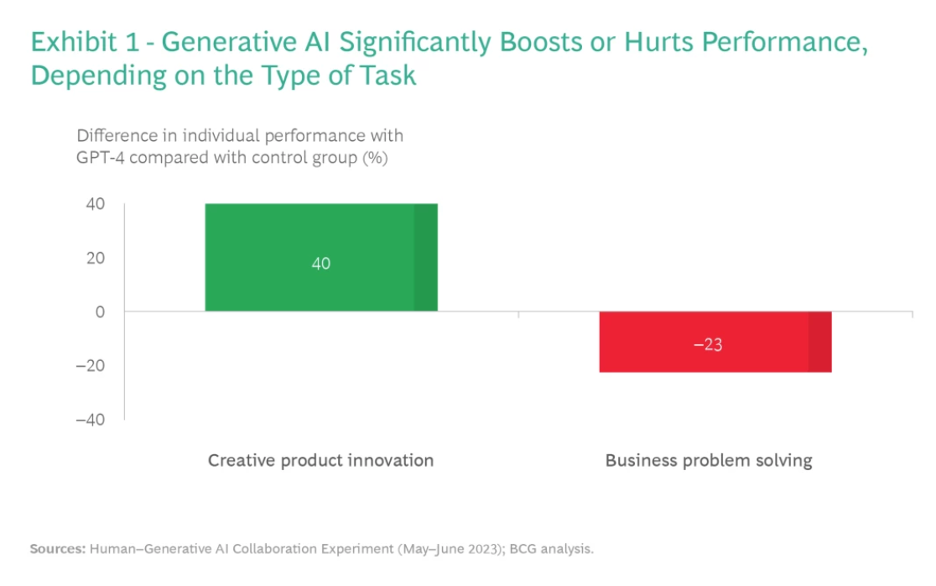
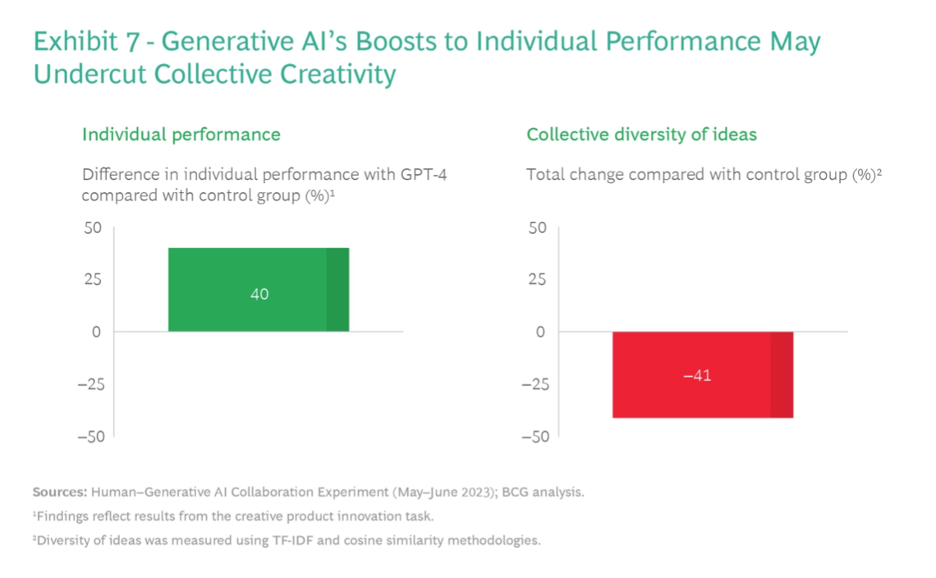
- GenAI significantly boosts performance in creative tasks, with a 40% increase in output quality compared to non-users.
- Conversely, for tasks like business problem-solving, outside GenAI’s current competency, performance dropped by 23%.
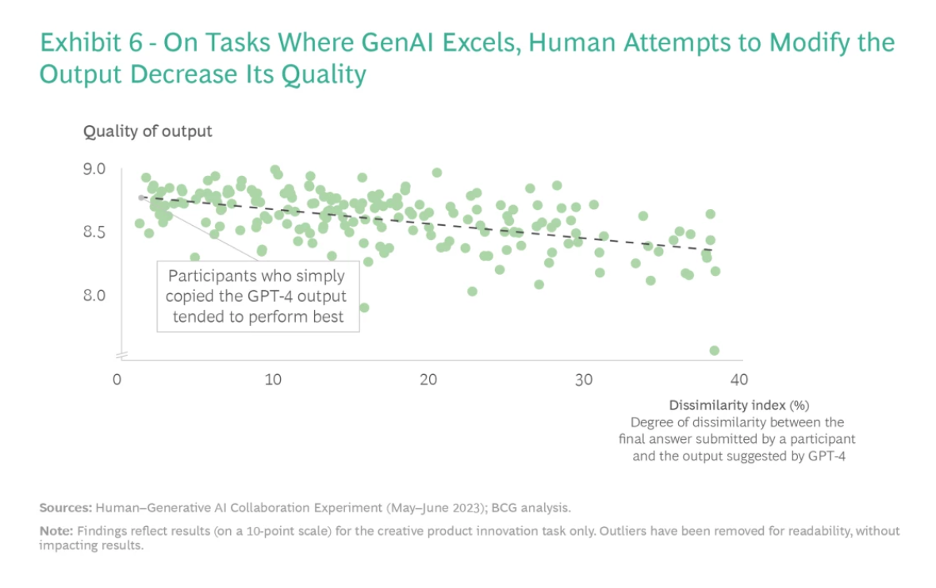
- The technology’s persuasive abilities lead to over-reliance, causing mismatches in task suitability and potential value destruction.
- GenAI’s uniform output can reduce a group’s diversity of thought by 41%, impacting collective creativity and innovation.
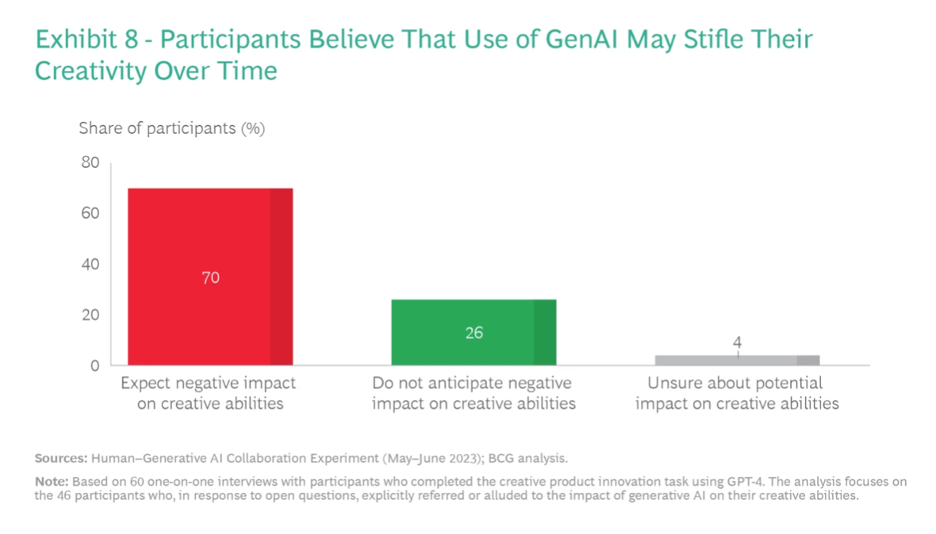
- Overuse of GenAI might diminish individuals’ creative skills over time, with about 70% of participants expressing this concern.
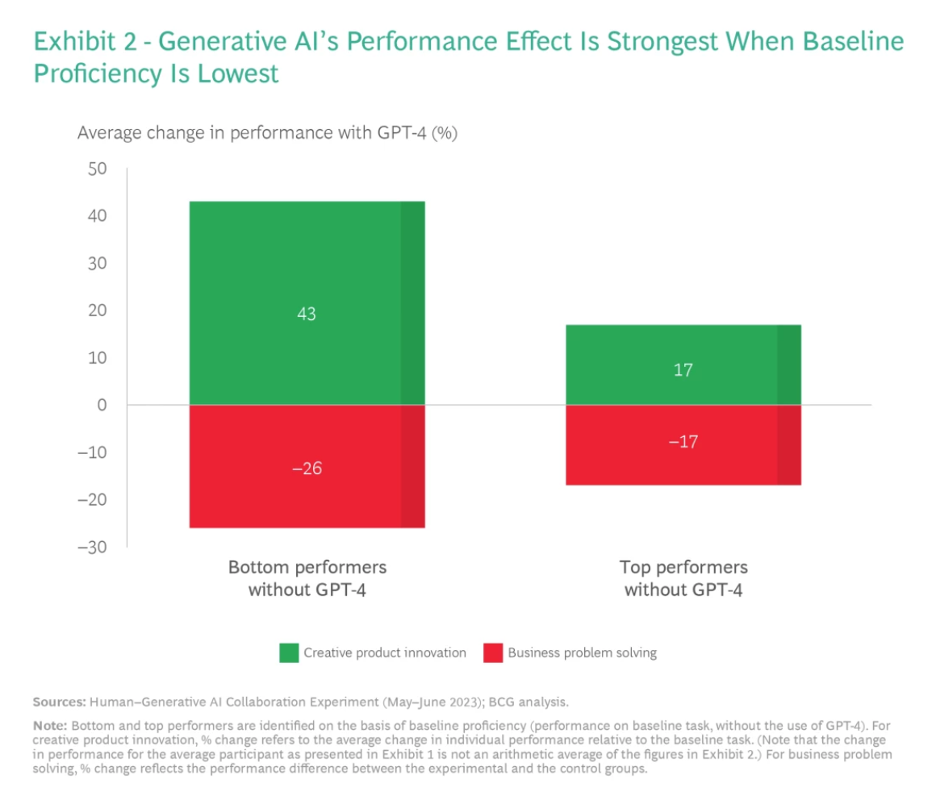
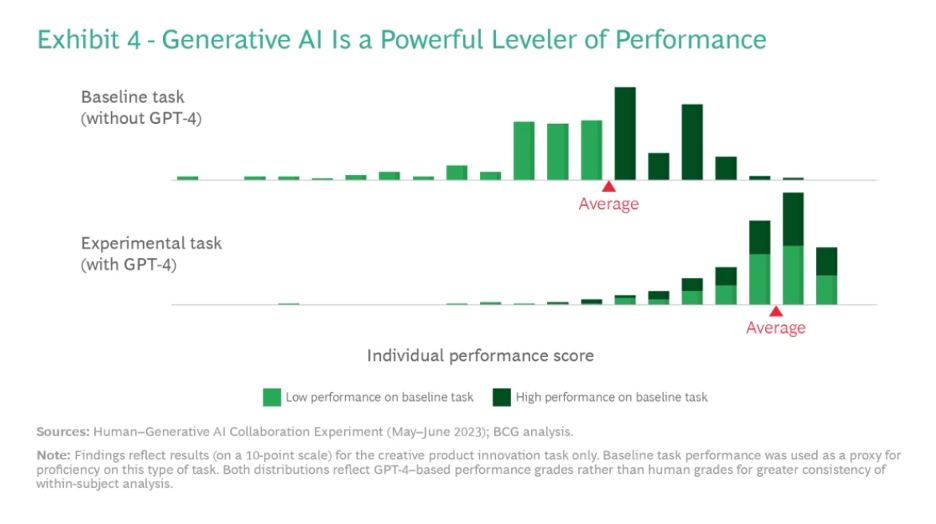
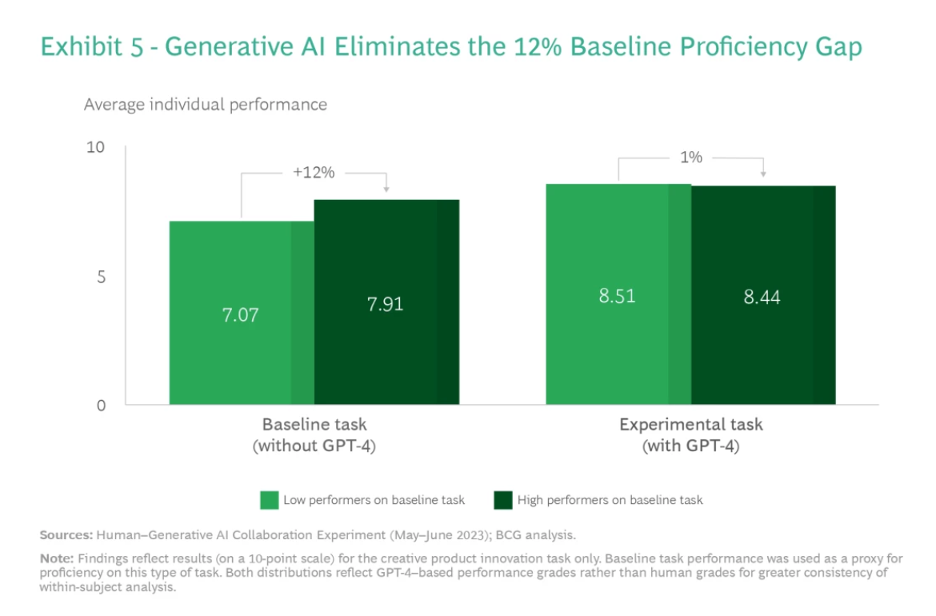
- The lower an individual’s baseline proficiency, the more significant GenAI’s impact, both positively in creative tasks and negatively in analytical tasks.
Recommendations:
- Organizations should critically assess which tasks are suitable for GenAI integration, focusing on creative enhancement while avoiding areas that require nuanced judgment.
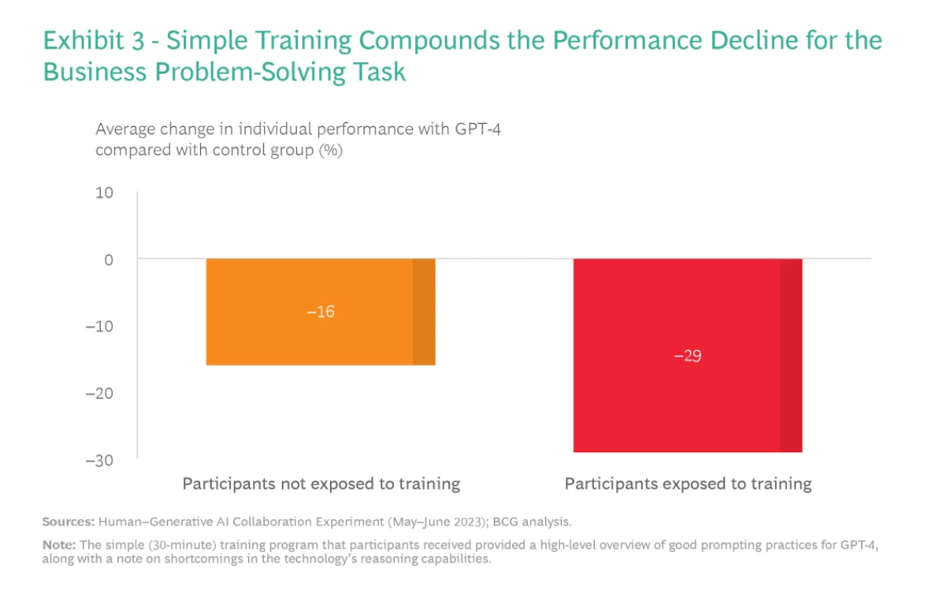
- The report suggests a continuous reevaluation of how GenAI is applied, taking into account the evolving capabilities of the technology.
- Developing a data strategy that tailors GenAI models with firm-specific data is advised to enhance differentiation and competitive advantage.
- It is necessary to redefine roles and workflows to capitalize on GenAI’s strengths, enabling employees to concentrate on higher-order tasks.
- Strategic workforce planning is essential to adapt to the changing requirements in the GenAI era, with a focus on fostering diverse thought and innovation capacities.
Thinking Critically
Implications:
- Companies that successfully integrate GenAI are likely to gain a considerable competitive advantage, which could potentially reshape market leadership and create a new class of AI-driven companies.
- Professions relying heavily on creative and innovative outputs may see an enhanced role of GenAI, necessitating a workforce skilled in AI collaboration and oversight.
- The improper application of GenAI could lead to significant value destruction for businesses, which implies a need for increased vigilance and understanding of GenAI’s capabilities and limitations
Alternative Perspectives:
- The methodology, primarily focused on a specific group of professionals, could limit the generalizability of the findings and recommendations.
- The recommendations may encourage an overreliance on GenAI, possibly overlooking the value of human intuition and decision-making in certain contexts, especially in complex, unpredictable situations.
- The rapid evolution of AI technologies might outpace the suggested recommendations, requiring continuous adaptation and possibly rendering some of the report’s conclusions obsolete in a short time.
AI Predictions:
- GenAI will likely become a pivotal tool in creative industries, enhancing collaboration between humans and AI, leading to innovative products and solutions.
- There will be an increased demand for roles that synergize human creativity with GenAI’s capabilities, leading to new career paths and the evolution of existing ones.
- Educational institutions might increasingly incorporate AI literacy and creative thinking in their curricula, preparing students for a workforce where GenAI plays a central role.
Glossary
- GenAI: Refers to Generative AI, a technology used for creative and problem-solving tasks in the study.
- Value Creation with AI: The process through which AI enhances business performance and innovation.
- Value Destruction: The negative impact of misusing or over-relying on AI technology in unsuitable tasks.
- Baseline Proficiency: The initial skill level of individuals before using AI, used to measure AI’s impact.
- Performance Boost: The improvement in task performance due to AI, quantified in the study.
- Diversity of Thought: The range of different ideas and perspectives in a group, which AI usage can impact.
- Task Suitability: Evaluating whether AI is appropriate for a specific task or problem.
- Prompt Engineer: A role that involves optimizing inputs for AI systems to generate desired outputs.
Figures
Members also get access to our comprehensive database of AI tools and fundraising



 Join hosts Anthony, Shane, and Francesca for essential insights on AI's impact on jobs, careers, and business. Stay ahead of the curve – listen now!
Join hosts Anthony, Shane, and Francesca for essential insights on AI's impact on jobs, careers, and business. Stay ahead of the curve – listen now!